RELATIVITY MEASUREMENTS WITH PRECISION BEYOND THE LIMITS
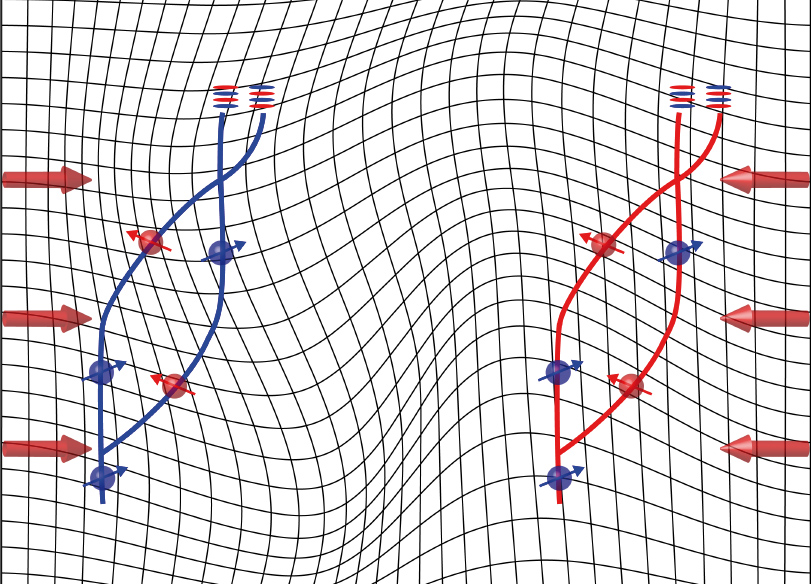 From quantum physics arrive two results that exceed the limits reached so far in sensitivity and precision in the measurements of the phenomena related to General Relativity and to gravitational physics. The results, published in Physical Review Letters were obtained in two atomic interferometry experiments by a team of researchers from the University of Florence and of INFN. At the base of the two experiments are atomic interferometry apparatuses, built in Florence, and based on the use of "atomic fountains" created with a laser. In the first experiment, carried out within the scope of the MAGIA Advanced project, the researchers developed a method that will allow testing of the validity of Einstein's equivalence principle with unprecedented accuracy. By cooling the rubidium atoms down to almost absolute zero with a laser and launching them upwards in a vacuum system, the conditions to measure the fall of weights were created by eliminating the effects due to the variation of the earth's gravity, which influence any classical measurement.Then, using strontium atoms, the researchers built a second experiment that proved to be valid for future measurement experiments, on a quantum scale, of low-frequency gravitational waves, with even higher sensitivities than those obtained by the LIGO and VIRGO interferometers. This second experiment thus opens the way to the construction of high precision atomic interferometry instruments to study gravitational waves in a region of frequency that cannot be observed with current terrestrial optical interferometers, instruments also useful for future spatial experiments in collaboration with the European Space Agency (ESA) and the Italian Space Agency (ASI).
From quantum physics arrive two results that exceed the limits reached so far in sensitivity and precision in the measurements of the phenomena related to General Relativity and to gravitational physics. The results, published in Physical Review Letters were obtained in two atomic interferometry experiments by a team of researchers from the University of Florence and of INFN. At the base of the two experiments are atomic interferometry apparatuses, built in Florence, and based on the use of "atomic fountains" created with a laser. In the first experiment, carried out within the scope of the MAGIA Advanced project, the researchers developed a method that will allow testing of the validity of Einstein's equivalence principle with unprecedented accuracy. By cooling the rubidium atoms down to almost absolute zero with a laser and launching them upwards in a vacuum system, the conditions to measure the fall of weights were created by eliminating the effects due to the variation of the earth's gravity, which influence any classical measurement.Then, using strontium atoms, the researchers built a second experiment that proved to be valid for future measurement experiments, on a quantum scale, of low-frequency gravitational waves, with even higher sensitivities than those obtained by the LIGO and VIRGO interferometers. This second experiment thus opens the way to the construction of high precision atomic interferometry instruments to study gravitational waves in a region of frequency that cannot be observed with current terrestrial optical interferometers, instruments also useful for future spatial experiments in collaboration with the European Space Agency (ESA) and the Italian Space Agency (ASI).



 Nicola Neri, a researcher at the INFN section in Milan, has been awarded one of the prestigious grants of the European Research Council (ERC) of almost 2 million euros with his SELDOM project, to be developed at the LHCb experiment at CERN's Large Hadron Collider, to investigate why our universe is made of matter rather than antimatter.The SELDOM project proposes a new experimental method to investigate the asymmetry between matter and antimatter, through the study of certain particular particles: heavy baryons. The distribution of the electrical charge of these particles has a spherical symmetry and their electric dipole moment - which measures the separation of electric charges of opposite sign - is predicted to be zero. One of the possible causes of the asymmetry between matter and antimatter in the universe could be linked to the not perfectly spherical shape of these particles, highlighted by the non-zero electric dipole moment. SELDOM is a competitive project at the international level: it is in fact part of an intense experimental research program of the electric dipole moment of the neutron, of the proton and of leptons, in progress worldwide, adding the new possibility of studying baryons containing heavy quarks, thanks to a new fixed target experiment, in which heavy baryons will be produced and then channelled into curved silicon and germanium crystals. This research could prove important because the eventual discovery of the electric dipole moment of a fundamental particle would represent clear evidence of physics beyond the Standard Model, i.e. of a new physics that goes beyond our current theories, and could tell us how it is possible that the universe exists, us included.
Nicola Neri, a researcher at the INFN section in Milan, has been awarded one of the prestigious grants of the European Research Council (ERC) of almost 2 million euros with his SELDOM project, to be developed at the LHCb experiment at CERN's Large Hadron Collider, to investigate why our universe is made of matter rather than antimatter.The SELDOM project proposes a new experimental method to investigate the asymmetry between matter and antimatter, through the study of certain particular particles: heavy baryons. The distribution of the electrical charge of these particles has a spherical symmetry and their electric dipole moment - which measures the separation of electric charges of opposite sign - is predicted to be zero. One of the possible causes of the asymmetry between matter and antimatter in the universe could be linked to the not perfectly spherical shape of these particles, highlighted by the non-zero electric dipole moment. SELDOM is a competitive project at the international level: it is in fact part of an intense experimental research program of the electric dipole moment of the neutron, of the proton and of leptons, in progress worldwide, adding the new possibility of studying baryons containing heavy quarks, thanks to a new fixed target experiment, in which heavy baryons will be produced and then channelled into curved silicon and germanium crystals. This research could prove important because the eventual discovery of the electric dipole moment of a fundamental particle would represent clear evidence of physics beyond the Standard Model, i.e. of a new physics that goes beyond our current theories, and could tell us how it is possible that the universe exists, us included.
 On 18 December, the Minister of Education, University and Research, Valeria Fedeli, went to CERN to visit the most important particle physics laboratory in the world, where there is so much Italy, with its physicists coordinated by INFN, and with the cutting-edge technologies developed by the national industry. The Minister, accompanied by CERN's Director General Fabiola Gianotti, and by INFN President Fernando Ferroni, leading the Italian delegation, visited the high technology laboratories and the ATLAS experiment at LHC and met the Italian community working at CERN at the Globe. Only three days earlier, at the end of the CERN Council meeting, the 25th anniversary of the LHC scientific program, started in 1992: indeed, when the previous LEP accelerator had just begun to "do physics" the new accelerator program was launche, had been celebrated. Since then, a lot of progress has been made and many important scientific and technological achievements have been made, including the historical discovery of the Higgs boson in 2012, earning the Nobel Prize for physics for Higgs and Englert the following year. The anniversary just celebrated testifies the extraordinary ability to plan the future, a characteristic of particle physics: even today, while the LHC, thanks to its very high performance, continues to churn out an impressive amount of valuable data, the physics community is working on its upgrade, the High Luminosity LHC, coordinated by the Italian Lucio Rossi, and is already studying the design of future of accelerator machines.
On 18 December, the Minister of Education, University and Research, Valeria Fedeli, went to CERN to visit the most important particle physics laboratory in the world, where there is so much Italy, with its physicists coordinated by INFN, and with the cutting-edge technologies developed by the national industry. The Minister, accompanied by CERN's Director General Fabiola Gianotti, and by INFN President Fernando Ferroni, leading the Italian delegation, visited the high technology laboratories and the ATLAS experiment at LHC and met the Italian community working at CERN at the Globe. Only three days earlier, at the end of the CERN Council meeting, the 25th anniversary of the LHC scientific program, started in 1992: indeed, when the previous LEP accelerator had just begun to "do physics" the new accelerator program was launche, had been celebrated. Since then, a lot of progress has been made and many important scientific and technological achievements have been made, including the historical discovery of the Higgs boson in 2012, earning the Nobel Prize for physics for Higgs and Englert the following year. The anniversary just celebrated testifies the extraordinary ability to plan the future, a characteristic of particle physics: even today, while the LHC, thanks to its very high performance, continues to churn out an impressive amount of valuable data, the physics community is working on its upgrade, the High Luminosity LHC, coordinated by the Italian Lucio Rossi, and is already studying the design of future of accelerator machines. Marica Branchesi, a scientist of the VIRGO collaboration, Associate Professor at the Gran Sasso Science Institute (GSSI) and associate researcher at INFN, has been included by the journal Nature in the 2017 ranking of the 10 personalties who have made the most significant contribution in the world of science. With the role of coordination between the LIGO and VIRGO interferometers and the electromagnetic telescopes network, Branchesi is one of the protagonists of the historic result announced jointly by the two collaborations, on 16 October 2017, of the first detection of gravitational waves from the fusion of two neutron stars: Branchesi was among the scientists who presented the result during the LIGO and VIRGO conference in Washington at the National Science Foundation (NSF), at the same time as many other conferences worldwide, including that in Italy of the INFN, of the National Institute of Astrophysics (INAF) and of the Italian Space Agency (ASI), in collaboration with the Ministry of Education, University and Research (MIUR). The observation of a gravitational wave signal from the fusion of two neutron stars, which took place simultaneously with the observation of the electromagnetic counterpart of this source, marked a historic change in our way of studying the universe with the beginning of the era of multi-messenger astronomy. Marica Branchesi is also chair of the gravitational wave commission of the International Astronomical Union and member of the Gravitational Wave International Committee.
Marica Branchesi, a scientist of the VIRGO collaboration, Associate Professor at the Gran Sasso Science Institute (GSSI) and associate researcher at INFN, has been included by the journal Nature in the 2017 ranking of the 10 personalties who have made the most significant contribution in the world of science. With the role of coordination between the LIGO and VIRGO interferometers and the electromagnetic telescopes network, Branchesi is one of the protagonists of the historic result announced jointly by the two collaborations, on 16 October 2017, of the first detection of gravitational waves from the fusion of two neutron stars: Branchesi was among the scientists who presented the result during the LIGO and VIRGO conference in Washington at the National Science Foundation (NSF), at the same time as many other conferences worldwide, including that in Italy of the INFN, of the National Institute of Astrophysics (INAF) and of the Italian Space Agency (ASI), in collaboration with the Ministry of Education, University and Research (MIUR). The observation of a gravitational wave signal from the fusion of two neutron stars, which took place simultaneously with the observation of the electromagnetic counterpart of this source, marked a historic change in our way of studying the universe with the beginning of the era of multi-messenger astronomy. Marica Branchesi is also chair of the gravitational wave commission of the International Astronomical Union and member of the Gravitational Wave International Committee. On 27 November at the University Foundation in Brussels, the NuPECC (Nuclear Physics European Collaboration Committee) presented its fifth Long Range Plan (LRP 2017) for Nuclear Physics in Europe, which takes into account the evolution of basic and applied research in this field and marks the stages of the programme for the coming years. NuPECC's mission, since its foundation in 1988, has been to formulate suggestions and recommendations for Nuclear Physics research in Europe, and for this purpose it has in the past developed four strategic reports (1991, 1997, 2004 and 2010). The final product of the process concluded in Brussels is the volume “NuPECC Long Range Plan 2017: Perspectives for Nuclear Physics”, containing recommendations for future developments in Nuclear Physics research, in the various infrastructures and in applications in this field, aimed at investigating key issues such as nuclear matter under different conditions, nuclear interactions and the origin of the elements. Information from nuclear physics on these topics is fundamental for the description of cosmological phenomena, such as neutron stars and their evolution, stellar explosions and energy production in stars. The LRP 2017 was presented in Brussels by the President of NuPECC, Angela Bracco, a Professor at the University of Milan and a researcher at the INFN Milan section, who emphasised, among other things, the leading position of Europe in this area and the collaborative effort among the various countries, crucial to maintaining such leadership. Among the 90 participants in the event, in addition to representatives of the INFN management and laboratories - with coordinating roles in the European nuclear physics programme - were ESFRI President Giorgio Rossi, ESFRI-PSE President, José Luis Martinez, the Head of the Research Infrastructures Unit of the European Commission, Ales Fiala, European Physical Society President, Rüdiger Voss, and FAIR Scientific Director, P. Giubellino.
On 27 November at the University Foundation in Brussels, the NuPECC (Nuclear Physics European Collaboration Committee) presented its fifth Long Range Plan (LRP 2017) for Nuclear Physics in Europe, which takes into account the evolution of basic and applied research in this field and marks the stages of the programme for the coming years. NuPECC's mission, since its foundation in 1988, has been to formulate suggestions and recommendations for Nuclear Physics research in Europe, and for this purpose it has in the past developed four strategic reports (1991, 1997, 2004 and 2010). The final product of the process concluded in Brussels is the volume “NuPECC Long Range Plan 2017: Perspectives for Nuclear Physics”, containing recommendations for future developments in Nuclear Physics research, in the various infrastructures and in applications in this field, aimed at investigating key issues such as nuclear matter under different conditions, nuclear interactions and the origin of the elements. Information from nuclear physics on these topics is fundamental for the description of cosmological phenomena, such as neutron stars and their evolution, stellar explosions and energy production in stars. The LRP 2017 was presented in Brussels by the President of NuPECC, Angela Bracco, a Professor at the University of Milan and a researcher at the INFN Milan section, who emphasised, among other things, the leading position of Europe in this area and the collaborative effort among the various countries, crucial to maintaining such leadership. Among the 90 participants in the event, in addition to representatives of the INFN management and laboratories - with coordinating roles in the European nuclear physics programme - were ESFRI President Giorgio Rossi, ESFRI-PSE President, José Luis Martinez, the Head of the Research Infrastructures Unit of the European Commission, Ales Fiala, European Physical Society President, Rüdiger Voss, and FAIR Scientific Director, P. Giubellino. 

